1 School of Computer and Electronic Information/School of Artificial Intelligence, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu, China
2 School of Physics and Technology, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu, China
The details of cross-sectional images based on Fourier domain optical coherence tomography play an important role that is limited to nonuniform sampling, spectral dispersion, inverse discrete Fourier transform (IDFT), and noise. In this section, we propose a method for emphasizing axial details to the greatest extent possible. After removing spectral dispersion, uniform discretization in the wavenumber domain is performed based on two interferograms via a specified offset in depth, with no spectrum calibration. The sampling number in IDFT is optimized to improve axial sensitivity up to 1.62 dB. The proposed process has the advantage of being based on numerical computation rather than hardware calibration, which benefits cost, accuracy, and efficiency.
optical coherence tomography image processing spectrum analysis image enhancement 激光与光电子学进展
2022, 59(18): 1836001
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Opto-Electronic Technology, School of Physics and Technology, Nanjing Normal University, Nanjing 210023, P. R. China
2 Center for Biomedical Engineering, School of Engineering, Brown University, Providence, Rhode Island, USA
3 Carney Institute for Brain Science, Brown University, Providence, RI 02906, USA
Optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) has emerged as an advanced in vivo imaging modality, which is widely used for the clinic ophthalmology and neuroscience research in the rodent brain cortex among others. Based on the high numerical aperture (NA) probing lens and the motion-corrected algorithms, a high-resolution imaging technique called OCT microangiography is applied to resolve the small blood capillary vessels ranging from 5 μm to 10 μm in diameter. As OCT-based techniques are recently evolving further from the structural imaging of capillaries toward spatio-temporal dynamic imaging of blood flow in capillaries, here we present a review on the latest techniques for the dynamic flow imaging. Studies on capillary blood flow using these techniques will help us better understand the roles of capillary blood flow for normal functioning of the brain as well as how it malfunctions in diseases.
Capillary vessel dynamics blood flow OCT angiography brain cortex micro-angiogram. Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2020, 13(1):
1 南京师范大学 物理与技术学院 江苏省光电技术重点实验室, 江南 南京210023
2 南京理工大学 电子工程与光电技术学院, 江南 南京 210094
3 江苏省地理信息资源开发与应用协同创新中心, 江南 南京210023
作为图像处理的一个重要手段, 边缘增强技术对振幅型和相位型物体成像有着重要的作用。而基于径向希尔伯特变换的涡旋滤波技术因其能够实现各向同性边缘增强倍受关注, 但传统的涡旋滤波由于中心奇点和锐利边缘引起的衍射会造成背景噪声的加剧和对比度的降低。近年来众多课题组针对涡旋滤波旁瓣抑制提出了种类各异的新型涡旋滤波器, 此外基于涡旋滤波的各向同性和各向异性边缘增强技术也得到了迅速发展。文中扼要地总结了近年来几种抑制涡旋旁瓣的方法, 包括拉盖尔高斯振幅调制、贝塞尔振幅调制、艾里振幅调制, 并从标量涡旋滤波和矢量涡旋滤波两个方面分别综述了各向同性和各向异性边缘增强的实现方法与研究进展。
旁瓣抑制 涡旋滤波 边缘增强 side lobe suppression vortex filtering edge enhancement 红外与激光工程
2019, 48(6): 0603015
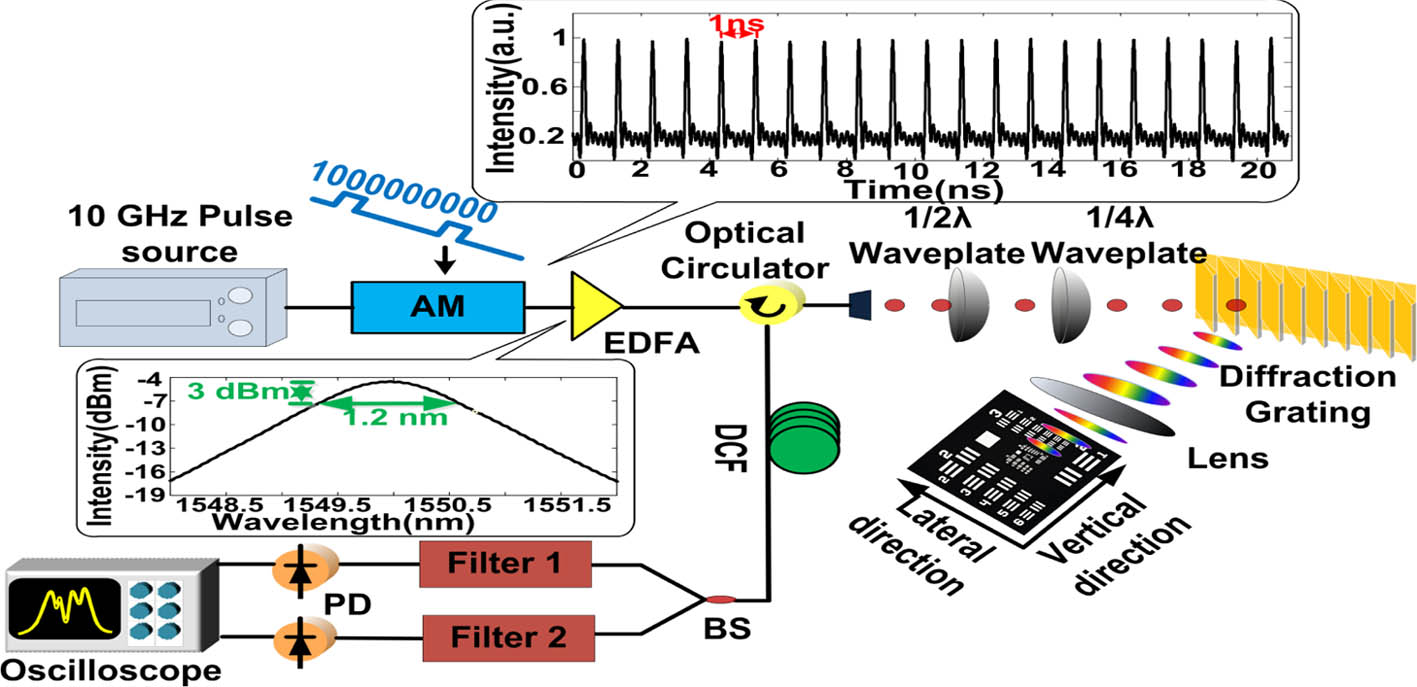
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Tsinghua National Laboratory for Information Science and Technology (TNList), Beijing 100084, China
2 Department of Electronic Engineering, Tsinghua University, Beijing 100084, China
A serial line scan microscopic imaging system with 1 GHz scan rate is proposed and demonstrated. This method is based on optical time-stretch in dispersive fiber to realize superfast scan imaging. Furthermore, a wavelength division technique is utilized to overcome the trade-off between high frame rate and spatial resolution caused by dispersion-induced pulse overlap. Every single frame is carved into two channels by optical filters and is detected in different wavelength bands separately. Then, both channels are combined to reconstruct the whole frame. By this method, an imaging system with spatial resolution of 28 μm at line scan rate of 1 GHz with chromatic dispersion of 1377 ps∕nm is realized. It has the potential to capture fast, nonrepetitive transient phenomena with a timescale of less than one nanosecond.
Imaging systems Microscopy Fiber optics components Photonics Research
2014, 2(4): 04000B31
1 清华大学电子工程系信息科学与技术国家实验室, 北京 100084
2 北京邮电大学电子工程学院信息光子学与光通信国家重点实验室, 北京 100876
报道了一种工作于1 μm波段、正常色散区、基于半导体可饱和吸收镜(SESAM)的被动锁模光纤激光器。激光器以高掺杂Yb光纤为增益物质,结合可调谐滤波器,形成环形腔结构。采用976 nm半导体激光器抽运,当抽运功率大于16 dBm时,激光器可实现1033~1069 nm波长范围内重复频率为25.4 MHz的宽带可调谐输出,性能稳定,在调谐范围内均可观测到非常规则的矩形输出光谱。在固定抽运功率下,对调谐范围内输出功率、光谱带宽、时域脉宽进行了实验测量和分析。在波长为1064 nm时,用单通道光栅对将谱宽为1.745 nm、时域脉宽为34.85 ps的脉冲压缩至15.45 ps。
光纤光学 光纤激光器 半导体可饱和吸收镜 可调谐 正色散 环形腔 脉冲压缩





